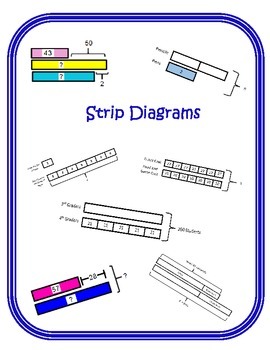
Strip Diagrams are a tool designed to help students solve math word problems accurately and efficiently. Students model mathematical relationships and identify known and unknown quantities. The model provides students with an image that organizes information and simplifies the problem solving process. By modeling the word problems, students develop strong reasoning skills which will help them as they transition to algebra. Students are familiar with problem solving maps, now they will use strip diagrams as a tool to solve problems.
Here are a couple of examples of solving problems with strip diagrams.
Strip Diagrams Broken Down Into Steps:
Step 1: Read the entire problem.
Alicia has $6 more than Bobby. If Bobby has $10, how much did they have altogether?
Step 2: Decided who is in the problem. Alicia and Bobby
Step 3: Decide what is involved in the problem. Money
Step 4: Draw unit bars: here we are drawing unit bars of equal length for each person to represent that they have the same amount of money.
Step 5: Read each sentence, 1 at a time to fill in the information.
Step 6: Put a ? in the place to show the information we need to find out. (When students are comfortable with the question mark switch to use a letter to represent the unknown)
Step 7: Write an equation and work computation to the side.
Step 8: Answer in a complete sentence to check for reasonableness.
Strip Diagrams Broken Down Into Steps:
Step 1: Read the entire problem.
Carlie sold 32 raffle tickets for the school fundraiser. That’s 4 times as many as many as Caroline sold. How many more raffle tickets did Carlie sell than Caroline?
Step 2: Decided who is in the problem. Carlie and Caroline
Step 3: Decide what is involved in the problem. Raffle tickets
Step 4: Draw unit bars: here we are drawing unit bars of equal length for each girl to remind us that are equal.
Step 5: Read each sentence 1 at a time to fill in the information.
Step 6: Put a ? in the place to show the information we need to find out. (When students are comfortable with the question mark switch to use a letter to represent the unknown)
Step 7: Write an equation and work computation to the side.
Step 8: Answer in a complete sentence to check for reasonableness.
32 tickets
Here are some videos working through some problems:
Strip Diagram Example
Strip Diagram Problems
Here is an activity we play at school that helps us practice strip diagrams:
Thinking Blocks
Let me know if you have any questions!